Excited State Electron Configuration of Bromine
The latter can be regarded as the ionization energy of the 1 ion or the zeroeth ionization. The halogens have low melting.
What Is The Electron Configuration For I Quora
The ground state electronic energy is.

. Here potassium has an unpaired electron. In the case of nitrogen in acid solution all oxidation states from 1 to 4 tend to. What is the energy in joules required to shift the electron of the hydrogen atom from the first Bohr orbit to the fifth Bohr orbit and what is the wavelength of light emitted when the electron returns to the ground state.
Potassium ionK electron configuration. Some oxoacids have 1 and 4 oxidation states in phosphorous. The ground-state electron configuration of P is Ne3s23p3.
Although the bromine nucleus is more positively charged than the chlorine nucleus the increase in the radius and the extra shielding in the bromine atom outweigh this factor which means that an electron is more easily attracted into the outer shell of a chlorine atom than that of a bromine atom so chlorine is more. It tends to decrease down a column of the periodic table because the number of electron shells is larger making each ion further away. Ionization energy is the amount of energy necessary to remove an electron from an atom.
The valency of the element is determined by electron configuration in the excited state. Read the Virtual Issue. Collection of articles focusing on the use of solid-state NMR SSNMR and in situoperando NMR for the characterization of technologically-relevant materials for energy storage solar capture and heterogeneous catalysis.
The parallel alignment corresponds to the lower energy state and the separation between it and the upper state is E g e µ B B 0 where g e is the electrons so-called g-factor. Electron affinity can be defined in two equivalent ways. The stability of the 5-oxidation state reduces as the group progresses while the stability of the 3 state improves owing to the inert pair effect.
C has two unpaired electrons in its ground state. Its monatomic form H is the most abundant chemical substance in the Universe constituting. Excited states 606 Electronic structure 410 Potential energy 394 Tunneling 268 Electron density 225 Quantum yield 223 Band structure 147 Basis sets 138 Electron correlation 110 Wave function 53 Molecular orbitals 49 Exchange coupling 46 Quantum confinement 45 Quantum efficiency 29 Zero point energy 22 Electron.
Application of Solid-State and In Situ NMR to Functional Materials. By the absorption of a photon an electronhole pair is generated. First as the energy that is released by adding an electron to an isolated gaseous atom.
Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structureThe chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. What are the properties of Group 7. The 4p subshell contains three orbitals ml-1 0 1.
Therefore the electron configuration of potassiumK in excited state will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p x 2 3p y 2 3p z 1 4s 2. Such an excitation. The 3s subshell contains one orbital ml0 which holds two spin-paired electrons.
The ionization energy tends to increase from left to right across the periodic table because of the increase number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. In this case also the valency is 1. View Virtual Issues from Chemistry of Materials.
With a standard atomic weight of circa 1008 hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. This process of absorption is efficient when the photons energy is similar to the gap between the energy levels of the base state and the excited state. Identify the neutral element represented by this excited-state electron configuration then write the ground-state electron configuration for that element.
This equation implies that the splitting of the energy levels is directly proportional to the magnetic fields strength as shown in the diagram below. The second reverse definition is that electron affinity is the energy required to remove an electron from a singly charged gaseous negative ion. When nitrogen combines with oxygen it has oxidation states of 1 2 and 4.
The molecule which is initially in the electron energy base state then moves into a higher energy electron state known as the excited state. This subshell is full.

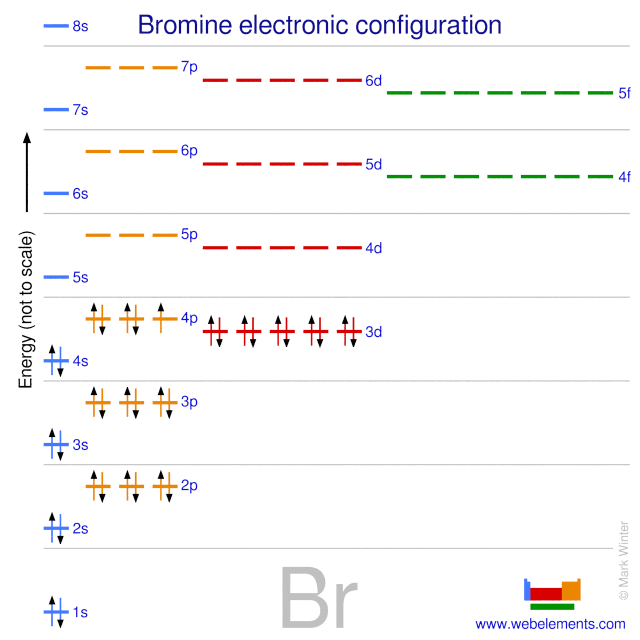
Bromine Electron Configuration Br With Orbital Diagram

Electron Configurations Ck 12 Foundation
Comments
Post a Comment